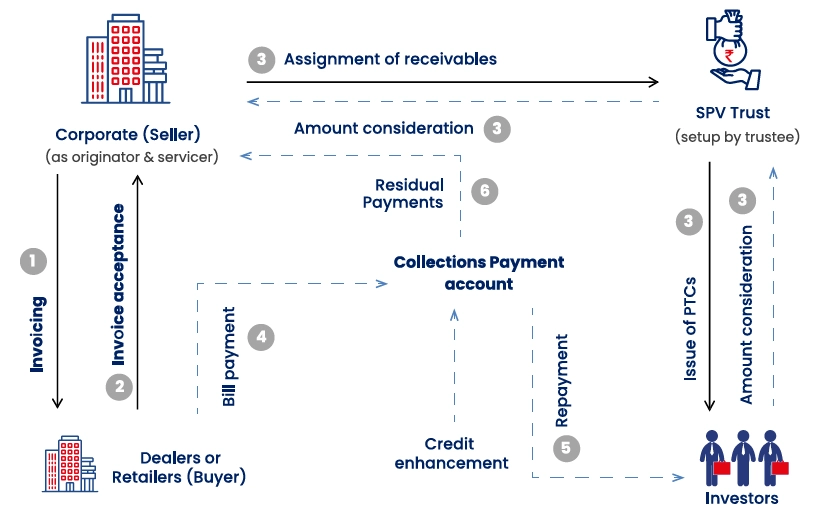
Supply Chain Finance
Building Supply Chain Resilience: Rethinking Finance & Procurement in 2025

The era of finance and procurement operating as isolated cost centers is over. Recent disruptions have forced these functions to collaborate strategically, with 59% of finance leaders reporting full integration between finance and procurement teams with shared systems and goals. This statistic was found in a recent webinar conducted by Vayana in collaboration with CFO Collective.
The Evolution from Cost Centers to Strategic Partners
For decades, procurement departments operated with a simple mandate: secure the lowest cost (L1) from suppliers. Finance teams, meanwhile, focused primarily on cost control and budget management. This siloed approach worked in stable market conditions, but today’s VUCA World has exposed its fundamental weaknesses.
A striking example emerged from A Leading player in electrical switches and sockets’ global operations, where an order shipped from Vietnam to the US experienced dramatic cost escalations during transit due to geopolitical factors. While customer contracts remained fixed, suppliers were forced to absorb unexpected cost increases – a scenario that perfectly illustrates why modern supply chains need integrated financial and procurement strategies.
As a panelist mentioned, “Procurement nowadays is not a mere cost center – it drives lots of value to the organization.” This fundamental shift reflects a broader transformation where the focus has moved from simple cost optimization to total value creation.
Understanding the New Procurement Paradigm
Modern procurement teams face complexities their predecessors never encountered. The traditional L1 approach fails to account for sophisticated risk calculations required in today’s market. Organizations now evaluate suppliers based on total cost of ownership, including:
- Long-term productivity gains : These are becoming central to supplier selection. A vendor charging 5-8% more initially might deliver significantly higher value over a 10-year asset lifecycle through superior technology, reliability, or innovation capabilities. Finance teams now partner with procurement to model these long-term benefits, justifying higher upfront costs based on ROI.
- ESG compliance requirements: ESG Mandates are reshaping supplier selection criteria entirely. Environmental, Social & Governance Standards are becoming competitive differentiators that affect long-term business sustainability, requiring financial modeling to balance compliance costs against risk mitigation and brand value protection.
- Geopolitical Risks: Wars and uncertainties have introduced new variables requiring constant recalibration. Initiatives like “Make in India” force organizations to balance higher short-term localization costs against long-term strategic benefits through sophisticated collaboration between finance and procurement teams.
Supply Chain Finance: From a Working Capital Management Tool to a Strategic Enabler
The evolution of supply chain finance mirrors the broader transformation in finance-procurement collaboration. What began as a simple cost-saving mechanism has become a core enabler of cash flow management and risk mitigation. Survey results show 58% of organizations now view supply chain finance as essential for cash flow management, while only 21% still see it as merely a cost-saving tool.
This transformation is particularly evident in industries with razor-thin margins. Another panelist captures this reality: “It’s impossible to get price hikes from customers while pressurizing suppliers to reduce costs. Financial Re-Engineering becomes the solution.”
Extending Support Beyond Tier-1 Suppliers
The most significant development in supply chain finance is recognizing that resilience requires supporting suppliers beyond immediate Tier-1 trade relationships. Tier-2 and Tier-3 suppliers often lack access to traditional credit facilities yet represent critical links that can cause significant disruptions if they fail.
Progressive organizations implement deep supply chain support through:
- Creating master agreements with supply chain finance providers to fund multiple supplier tiers
- Extending liquidity support to prevent downstream disruptions
- Implementing early warning systems providing health scores for all vendor relationships
Technology as the Catalyst for Integration
Digital transformation of supply chain finance is accelerating rapidly. Vayana-CFO Collective webinar revealed that 43% of finance leaders operate with semi-automated processes including manual interventions, while 22% have achieved fully digitized systems with end-to-end automation.
Organizations with advanced digital integration report:
- Real-time supplier financial health visibility
- Automated risk assessment and early warning capabilities
- Seamless ERP integration
- Financing approvals in as little as 15 minutes
The next frontier involves AI-powered solutions offering predictive supplier failure identification, dynamic risk-based pricing models, and automated financing decisions that reduce manual intervention while future-proofing businesses.
New-age fintechs like Vayana are fundamentally changing the lending landscape by moving beyond traditional balance sheet-based assessments to cash flow-based models. This shift particularly benefits SMEs with strong trading relationships and reliable cash flows but weaker traditional financial statements.
Overcoming Implementation Challenges
Despite clear benefits, organizations face several obstacles:
- Balancing short-term pressures with long-term value creation remains challenging. Organizations struggle to justify investments in supplier relationships when facing immediate cost pressures. Schneider Electric provides a practical example, moving from traditional L1 procurement metrics to project-level cash flow positivity, evaluating whether paying a vendor 5% more upfront delivers better 10-year productivity.
- Limited risk visibility across multi-tier supply chains poses significant challenges. Traditional supplier assessment methods prove inadequate for understanding complex supply chain interdependencies, requiring comprehensive technology solutions.
- Budget constraints often limit required technology investments. However, innovative financing structures can address this. Vayana works with corporates to ring-fence their supply chain ecosystems where different supplier segments receive appropriate financing solutions: 20%-30% of top suppliers receive traditional financing, another 30% get NBFC funding, and the remaining tier receives fintech-based solutions.
Looking ahead, the next wave involves Embedded Finance Solutions seamlessly integrated into business processes, including tokenization and smart contracts for automated payment triggers, trade receivables securitization, and private credit markets complementing traditional banking for mid-tier suppliers.
India is emerging as a global leader in Supply Chain Finance innovation, with multinationals using India as a testing ground for solutions later implemented worldwide.
Key Implementation Metrics and Success Measures
Successful organizations move beyond traditional cost-focused metrics to implement shared KPIs between finance and procurement teams. Leading companies create unified vendor databases serving as single sources of truth, including payment terms, performance history, and financial indicators.
Modern success metrics encompass:
- Supplier financial health scores
- Supply chain continuity measurements
- Optimized cash conversion cycles
- Innovation contribution tracking
These integrated KPIs require both teams to collaborate on vendor selection, moving beyond the traditional L1 approach.
The Path Forward: Building Ecosystem Resilience
Modern supply chain resilience requires a fundamental shift from transactional thinking to ecosystem-wide strategic planning. Rather than simply pushing cost reductions down the chain, progressive organizations help vendors invest in productivity improvements through supply chain financing, creating sustainable competitive advantages.
Finance and procurement teams are now co-architects of organizational resilience, designing integrated systems that drive sustainable growth in an increasingly complex global marketplace.